4.3 What is Non-Farm Payrolls
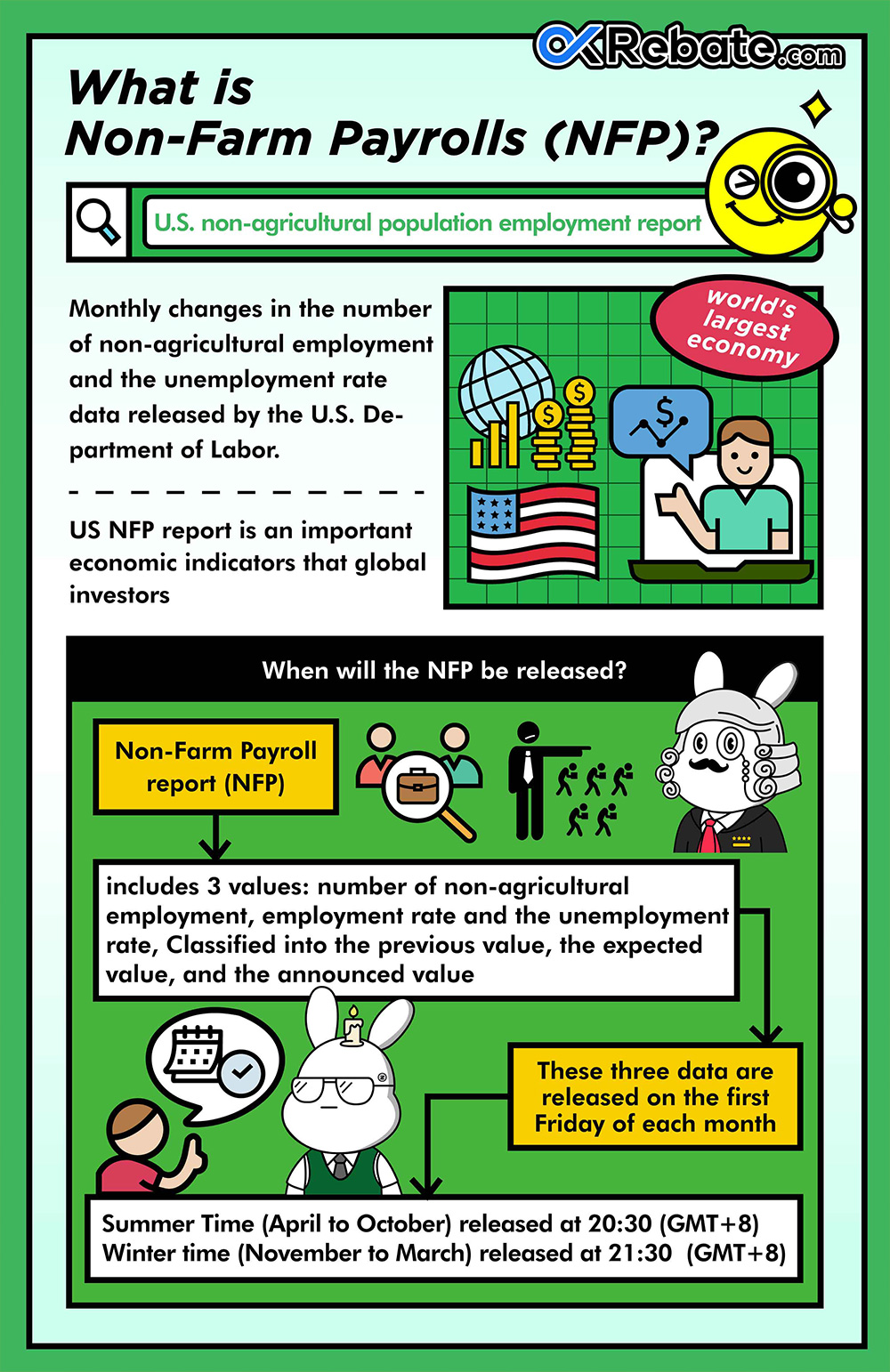
What is Non-Farm Payroll (NFP) Data?
Non-Farm Payroll, known as NFP, refers to the monthly employment report released by the U.S. Department of Labor. It provides data on changes in non-farm employment numbers and the unemployment rate in the United States. Because the United States is the world’s largest economy, NFP data is considered one of the crucial economic indicators monitored by global investors.
When is NFP Data Released?
The Non-Farm Payroll report includes three key figures: non-farm employment, the employment rate, and the unemployment rate. These figures are reported with previous values, expectations, and actual values. The report is typically released on the first Friday of each month, following Eastern Time. During daylight saving time (from April to October), it is usually released at 8:30 AM, while during standard time (from November to March), it is released at 9:30 AM.
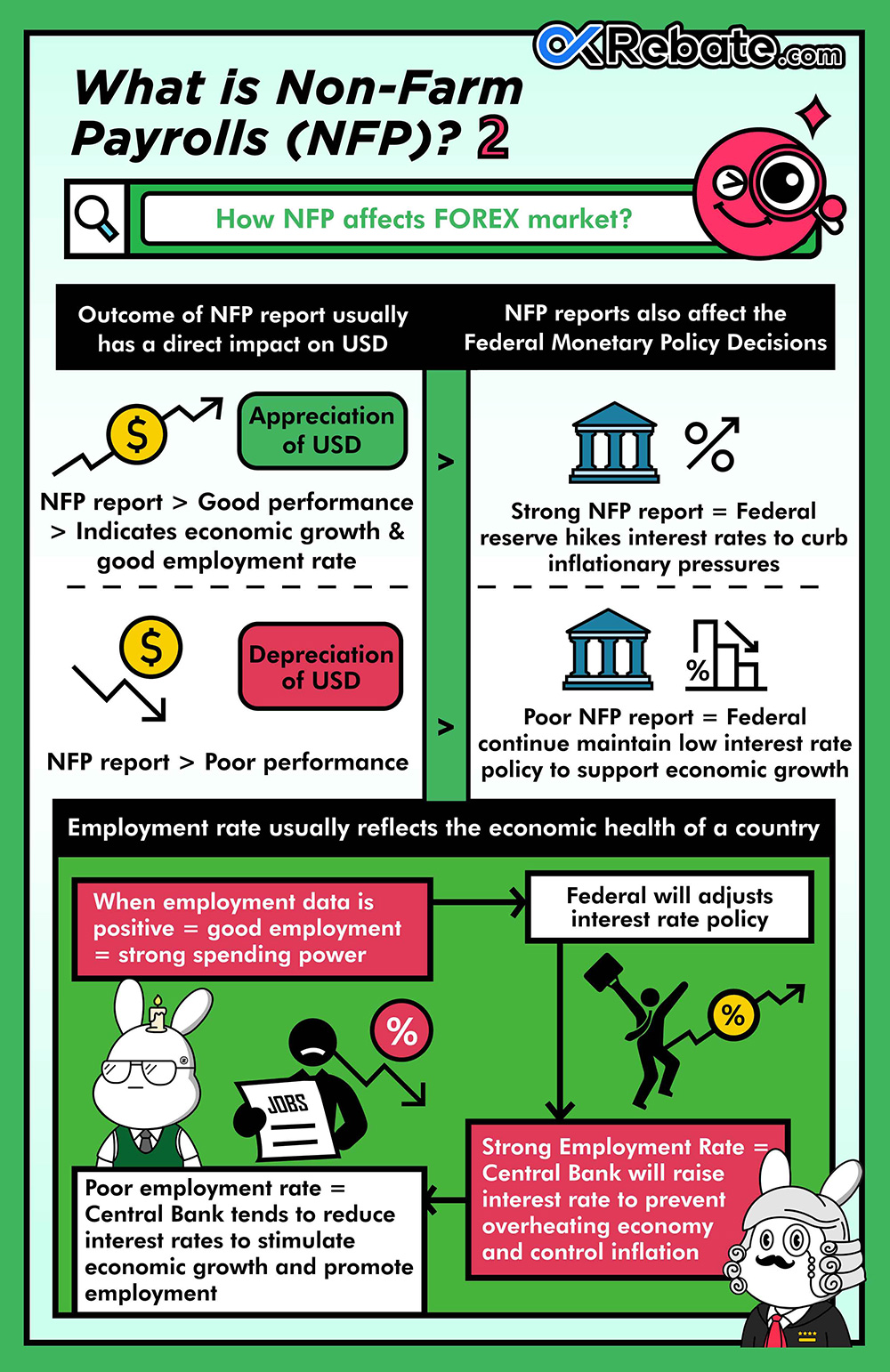
How Does NFP Data Impact the Forex Market?
The quality of NFP data typically has a direct impact on the U.S. dollar. If NFP data performs well, indicating strong economic growth and a robust job market, it often leads to the appreciation of the U.S. dollar. Conversely, if NFP data underperforms, it may result in the depreciation of the U.S. dollar.
NFP data can also influence the monetary policy decisions of the Federal Reserve. Strong NFP data may prompt the Federal Reserve to consider raising interest rates to curb inflationary pressures. In contrast, weak NFP data may lead the Federal Reserve to maintain its low-interest-rate policy to support economic growth.
Employment data is a key indicator for assessing economic conditions because the employment rate often reflects a country’s economic health. When employment data is strong, indicating a healthy job market where more people are finding work, it leads to increased consumer spending and economic activity. Therefore, the Federal Reserve evaluates the current economic situation and adjusts interest rate policies accordingly based on employment data.
Generally, when the job market is robust, and labor market conditions improve, central banks tend to raise interest rates to prevent the economy from overheating and to control inflation. When interest rates rise, the cost of borrowing increases, which can slow down consumer and investment spending. This tightening of monetary policy helps balance the economy and maintain inflation within a manageable range.
When employment data is weak, central banks tend to lower interest rates to stimulate economic growth and promote employment. Lower interest rates reduce the cost of borrowing, potentially encouraging consumer and investment spending, which, in turn, drives economic growth. This accommodative monetary policy can help reduce unemployment rates and stimulate economic growth.
In summary, Non-Farm Payroll data is a highly important economic indicator for investors as it provides crucial information about the U.S. economy and job market. It has a significant impact on the U.S. dollar’s value, as well as influencing monetary policy decisions. Therefore, investors who focus on fundamental analysis should pay close attention to this indicator.