4.1 What is Forex Fundamental Analysis
Technical analysis and fundamental analysis are two main studies in financial market analysis. Technical analysis primarily predicts future market trends by studying technical indicators such as price movements and trading volume. On the other hand, fundamental analysis focuses on economic fundamental factors, such as a country’s monetary policy, economic data, political situations, and geopolitical conditions. In this chapter, we will provide a detailed introduction to fundamental analysis.
Analysts who believe in fundamental analysis think that changes in currency exchange rates are influenced by fundamental factors. Therefore, by analyzing these factors, it is possible to predict the future trends of currency exchange rates.
The rough classification and explanation of fundamental analysis in Forex are as follows:
In Forex fundamental analysis, analysts typically concentrate on several key factors: monetary policy, key national economic data, geopolitical factors, and international trade.
Monetary Policy: This includes central bank interest rate decisions and currency supply.
- Interest Rate Decisions: Central banks determine the level of interest rates, which is a crucial component of monetary policy. By adjusting interest rates, central banks can influence factors like liquidity in the currency market, exchange rates, and inflation. If a country’s interest rates rise, it usually attracts more capital inflow, increasing demand for the country’s currency and leading to currency appreciation.
- Currency Supply: This measures the total amount of currency in circulation within an economy and is typically measured through indicators like M1 and M2. Excessive currency supply can lead to inflation, as the purchasing power of the currency decreases. This may result in reduced trust in the currency by domestic and foreign investors, ultimately causing a depreciation of the exchange rate. Conversely, insufficient currency supply can lead to deflation, as increased purchasing power may result in falling prices, higher production costs for businesses, and potentially higher unemployment rates.
Key National Economic Data: This includes GDP, CPI, unemployment rate, trade balance, and other economic indicators.
- Gross Domestic Product (GDP): GDP represents the total value of all final goods and services produced within a country and serves as an indicator of the overall economic performance. If a country’s GDP growth is robust, it usually signifies economic prosperity, increasing demand for its currency and leading to currency appreciation.
- Consumer Price Index (CPI): CPI measures the average price changes of a basket of goods and services related to people’s daily lives. It is commonly used to gauge the level of inflation in a country. The CPI’s rate of change reflects to some extent the extent of inflation or deflation. Broad and sustained price increases are typically considered inflation, while broad and sustained price decreases indicate deflation.
- Unemployment Rate: This measures the extent of labor market slack in a country and is typically used to assess the impact of economic conditions and policies. A decrease in a country’s unemployment rate usually implies stable economic growth, increasing demand for its currency and leading to currency appreciation.
- Trade Balance: This measures the difference between a country’s imports and exports. If a country’s trade balance is strong, it generally increases demand for its currency, leading to currency appreciation.
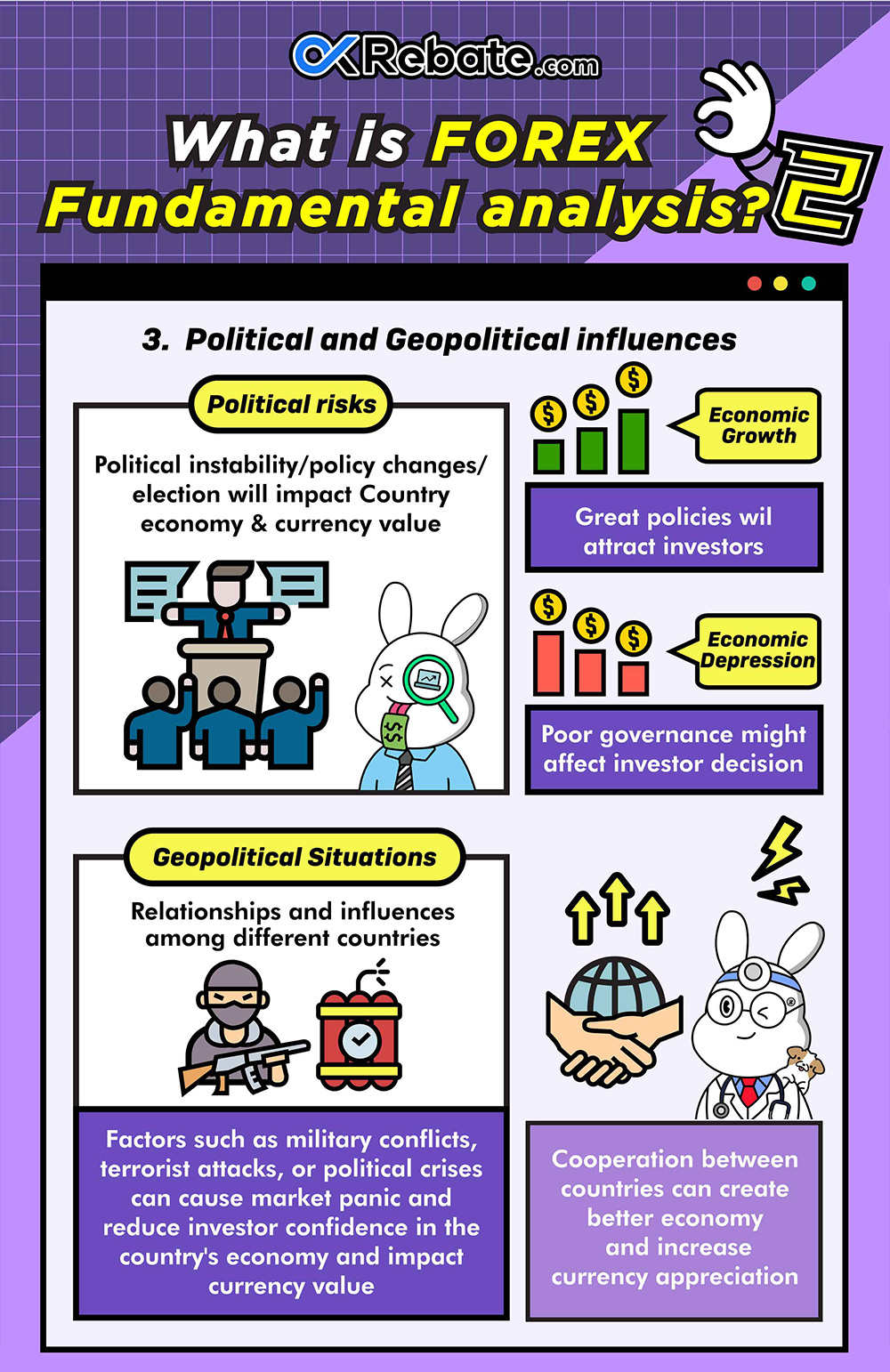
Political Risk and Geopolitical Situations:
- Political risk typically refers to political instability or policy changes. Political turmoil can decrease investor confidence in a country’s economy and currency, leading to currency depreciation. Events like elections, which may result in policy changes, can also impact a country’s economy and currency.
- Geopolitical situations typically refer to relationships and influences between different countries, which can be political, economic, or military. Events such as military conflicts, terrorist attacks, or political crises can cause market panic, reduce investor confidence in a country’s economy and currency, and lead to currency depreciation.
The above fundamental factors are typically monitored by Forex traders and analysts. We can keep an eye on changes in these economic indicators and news data to better predict market trends and formulate trading strategies. It’s important to note that the impact of economic indicators from different countries is highly complex and interrelated, and investors need to consider multiple factors when determining their influence on the Forex market.